Diabesity is a new term used to describe the combination of obesity and type 2 diabetes which are two worldwide epidemic affecting hundreds of millions of patients. Diabesity is an important public health issue1 and could reduce a person's life expectancy by more than 20 years2.
According to the CDC, WHO, World Diabetes Foundation, American Diabetes Foundation and other official organisations, more than 700 million adults suffer from obesity and more than 450 million adults suffer from type 2 diabetes. China has the largest population of diabetics in the world and approximately 16% of adults are obese3, making it the largest potential market for weight loss and diabetes treatment in the world.
At this stage, innovative GLP-1 drugs have shown convincing results in diabetic patients and in patients suffering from obesity, but the drugs need to be administered indefinitely4. This is a huge challenge for adherence and cost for patients. For example, patients in the US will spend approximately $1,300 per month on GLP-1 medication, which would amount to over $15,000 per year. Furthermore, the new innovative GLP-1 drugs do not seem to be as effective for weight loss in patients who suffer from both obesity and diabetes and are therefore not the answer for the diabesity patient population.
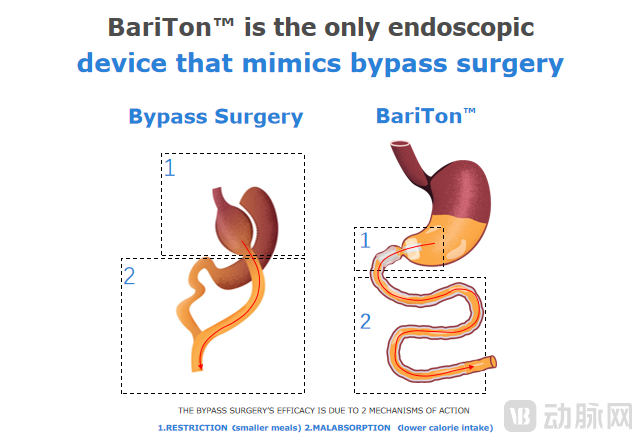
The only sustainable option for diabesity remission is bypass surgery, which involves the removal of part of the stomach to reduce its volume and creating a bypass by cutting the bowels and connecting a distal section of the bowels to the newly formed stomach so that the food bypasses the proximal bowels.
By reducing the size of the stomach, a restriction is created leading patients to eat less and feel full for a longer duration, and by bypassing the proximal bowels, food does not mix with the biliopancreatic juices leading to malabsorption and less calory intake. And so during each meal, the patient eats less, feels full for a longer period of time, and absorbs fewer calories.
Surgery requires general anesthesia, it is traumatic to the patient, it is irreversible, and it may bring long-term complications.
Vcbeat recently interviewed a French company, BariaTek™ Medical, which has developed the BariTon™, the world's first non-invasive endoscopic implant that mimics bypass surgery, the most efficient intervention for the treatment of diabesity. BariTon™ mimics bypass surgery such that it restricts the stomach, via an innovative inflatable portion, and allows the food to bypass the proximal bowels via a proprietary food liner. The result is smaller meals, longer satiety, and a lower calorie intake per meal thus, similar to bypass surgery, leading to substantial weight loss and an improved metabolic profile.
Youssef Biadillah, CEO of BariaTek™, is a 20-year veteran in the medical device industry with an impressive track record of developing successful minimally invasive medical devices, he was an early employee at Baylis Medical company in Toronto Canada, acquired by Boston Scientific for $ 1.75 billion, Sadra Medical in Silicon Valley in the USA, acquired by Boston Scientific for $ 450 million, and Symetis in Geneva area Switzerland, also acquired by Boston Scientific for $ 435 million. When talking about the reason for joining BariaTek™, he told us that after spending those years developing medical devices, he has always wanted to work on diabesity because he realized it was the most common denominator in patients he treated for pain, spine, and cardiovascular diseases. Truffle Capital, a premier European venture capital firm, based in Paris decided to start a company to address obesity and so this is how he joined the adventure as the first employee and Chief Executive Officer of the company.
Youssef's philosophy in terms of product development is that "time is the most expensive commodity", so when building the team at BariaTek™, he looks for a balance between solid medical device experience and enthusiasm for innovation and improving patients' lives. Having both extensive experience in developing innovative medical devices and maintaining a passion for creating medical devices that improve quality of life, the combination of talented people from around the world has produced great results for the company in a relatively short period of time based on the constant pursuit of purposefulness and efficiency.
Currently, BariTon™ has completed its product design and pre-clinical animal studies and is scheduled to launch its clinical trials in Q3 of 2023.
The BariTon™ is the first endoscopic non-invasive and reversible technology that mimics the bariatric bypass procedure and is performed without any traumatic elements such as needles sutures or staples, the BariTon™ is implanted via a dedicated endoscope in under 20 minutes in patients and doesn’t necessitate general anesthesia. Unlike surgery, it is an ambulatory procedure where patients can come into the clinic in the morning and leave in the afternoon.
The BariTon™ device is composed of two portions, a trans-pyloric inflatable portion and a food liner positioned in the bowels. The former, through a non-atraumatic IP-protected anchoring method, is able to slow down gastric emptying and enhance satiety, allowing patients to eat less, fill up faster, and feel hungry later. The latter, the liner, prevents the food from mixing with the biliopancreatic juices in the proximal bowels and delays food absorption leading therefore to less calorie intake and better control of blood sugar levels.
The BariTon™ is delivered endoscopically without the need for general anesthesia, so through the mouth, in a 20-minute procedure without the use of sutures nor staples, resulting in negligible trauma to the patient at the time of implantation.
What's even more attractive is that the procedure is reversible with no alteration to the patient's anatomy. Indeed, the BariTon™ is fully retrievable if need be in less than 10 minutes.
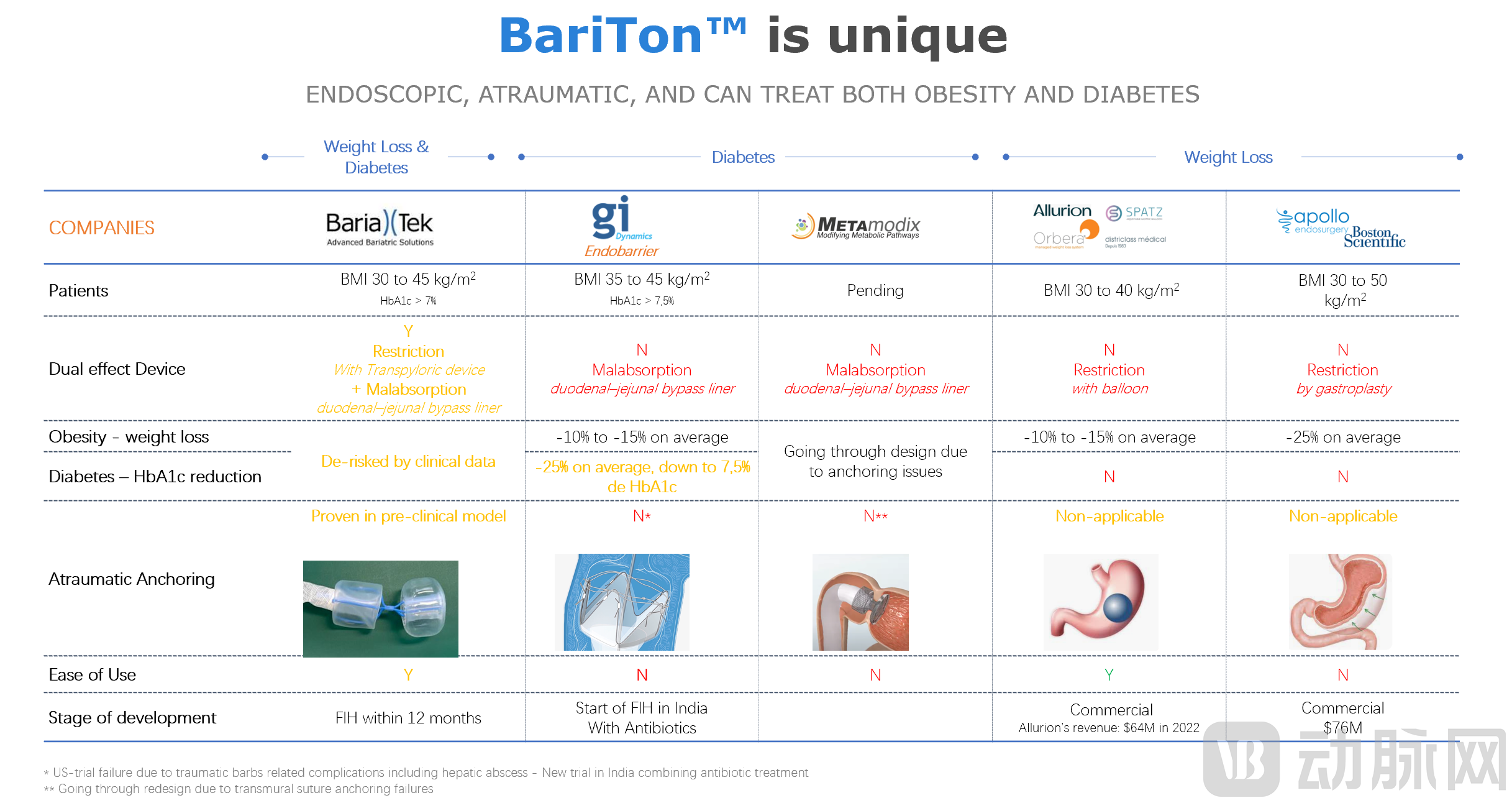
With outstanding performance in terms of innovation, safety, efficacy and stability, BariaTek™ Medical is scheduled to launch its clinical trials and initiate patient enrollment within the third quarter of 2023. Bariatek is presently going through a fundraising effort to have the liquidities necessary to fund the clinical development and continue the development towards a commercial launch.
The first human trial will focus on individuals aged 30-65 years with a BMI between 30-45 including patients with type 2 diabetes.
Youssef is convinced that the BariTon™ is a disruptive and sustainable solution for the treatment of diabesity. Just as cardiac stents have replaced coronary bypass surgery, the BariTon™ will replace metabolic bariatric surgery.
BariaTek™ is cooperating with clinical and commercial partners worldwide and expects to complete global commercial transformation within 3-5 years, their goal is to become the world leader in the treatment of obesity and diabetes via endoscopic minimally invasive ways.
During the interview, Youssef clearly expressed his high interest in China. In fact, BariaTek™ Medical is in discussions with various Chinese players to find the best way to set-up operations in China including clinical trials to confirm the safety of efficacy of the BariTon™ device for Chinese patients and offer the BariTon™ to the Chinese patient population as a sustainable minimally invasive and reversible alternative to treat obesity and diabetes.
On a personal level, Youssef has travelled extensively in China in the last 25 years and has visited many cities and regions including Beijing, Shanghai, Xi'an, Wuhan, Chengdu, Guilin, and Harbin. Through his travels in China, Youssef gained a richer and more diverse understanding of China its culture and its people and he hopes to have fruitful collaborations in China and be able to offer the BariTon™ as a sustainable minimally invasive solution for Chinese patients suffering from obesity and diabetes.
References:
1. Ng, A.C.T., Delgado, V., Borlaug, B.A. et al. Diabesity: the combined burden of obesity and diabetes on heart disease and the role of imaging. Nat Rev Cardiol 18, 291–304 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-020-00465-5
2. Nianogo RA and Arah OA (2022) Forecasting Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Incidence and Burden: The ViLA-Obesity Simulation Model. Front. Public Health 10:818816doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022818816
3. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2021; 9: 373-92
4. Wilding, JPH, Batterham, RL, Davies, M, et al. Weight regain and cardiometabolic effects after withdrawal of semaglutide: The STEP 1 trial extension. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022; 24( 8): 1553- 1564. doi:10.1111/dom.14725
